实现方案
- 在img元素时, 自定义一个属性data-src,用于存放图片的地址
- 获取屏幕可是区域的尺寸
- 获取元素到窗口边缘的距离
- 判断元素是否在可视区域内.在则将data-src的值赋给src,否则不执行其他操作
实质
当图片在可视区域内时,才加载,否则不加载;也可一个给个默认的图片占位
用到的api
IntersectionObserver它提供了一种异步观察目标元素与顶级文档viewport的交集中的变化的方法window.requestIdleCallback()方法将浏览器的空闲时段内调用的函数排队. 这使开发者在主事件循环上执行后台和底优先级工作, 而不会影响延迟关键事件, 如动画和输入响应
几个细节
- 提前加载,可以+100 像素
- 滚动时只处理未加载的图片即可
- 函数节流
简单代码示例
判断是否是在可视区域的三种方法
- 屏幕可视区域的高度 + 滚动条滚动距离 > 元素到文档顶部的距离
document.documentElement.clientHeight + document.documentElement.scrollTop > element.offsetTop- 使用getBoundingClientRect() 获取 元素大小和位置
- IntersectionObserver 自动观察元素是否在可视区域内
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>图片懒加载</title>
<style>
img {
display: block;
height: 450px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
border: 1px solid blue;
width: 450px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<img data-src="./images/1.png" alt="" />
<img data-src="./images/2.png" alt="" />
<img data-src="./images/3.png" alt="" />
<img data-src="./images/4.png" alt="" />
<img data-src="./images/5.png" alt="" />
<img data-src="./images/6.png" alt="" />
</body>
<script>
var imgs = document.querySelectorAll('img')
// 节流函数, 定时器版本
function throttle(func, wait) {
let timer = null
return (...args) => {
if (!timer) {
func(...args)
timer = setTimeout(() => {
timer = null
}, wait)
}
}
}
// H + S > offsetTop
function lazyLoad1(imgs) {
// offsetTop 是元素与offsetParent 的距离, 循环获取直到页面顶部
function getTop(e) {
var T = e.offsetTop
while ((e = e.offsetParent)) {
T += e.offsetTop
}
return T
}
var H = document.documentElement.clientHeight // 获取可视区域的高度
var S =
document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTop
// + 100 像素 提前100个像素就开始加载
// 并且只处理没有src即没有加载过的图片
Array.from(imgs).forEach((img) => {
if (H + S + 100 > getTop(img) && !img.src) {
img.src = img.dataset.src
}
})
}
const throttleLazyLoad1 = throttle(lazyLoad1, 200)
function lazyLoad2(imgs) {
function isIn(el) {
var bound = el.getBoundingClientRect()
var clientHeight = window.innerHeight
return bound.top <= clientHeight + 100
}
Array.from(imgs).forEach((img) => {
if (isIn(img) && !img.src) {
img.src = img.dataset.src
}
})
}
const throttleLazyLoad2 = throttle(lazyLoad2, 200)
// 监听滚动事件
window.onload = window.onscroll = () => {
// throttleLazyLoad1(imgs)
throttleLazyLoad2(imgs)
}
function lazyLoad3(imgs) {
const io = new IntersectionObserver((ioes) => {
ioes.forEach((ioe) => {
const img = ioe.target
const intersectionRatio = ioe.intersectionRatio
if (intersectionRatio > 0 && intersectionRatio <= 1) {
if (!img.src) {
img.src = img.dataset.src
}
}
img.onload = img.onerror = () => io.unobserve(img)
})
})
imgs.forEach((img) => io.observe(img))
}
// lazyLoad3(imgs)
</script>
</html>API说明
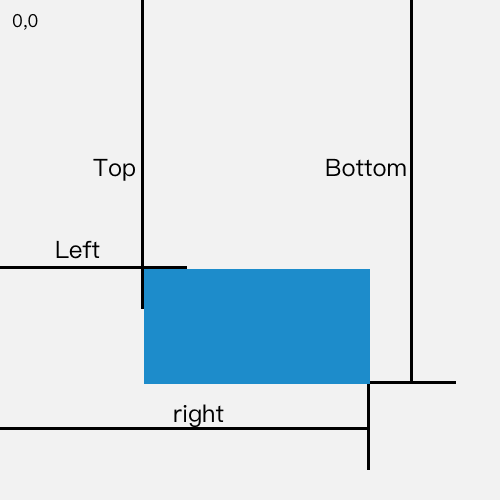
getBoundingClientRect
- 返回值是一个DOMRect对象, 这个对象是由该元素的getClientRects() 方法返回的一组矩形的集合, 就是该元素的css边框大小.返回的结果是包含完整元素的最小矩形,并且拥有 left,top,right,bottom,x, y, width, height 这几个以像素为单位的只读属性用于描述整个边框, 除了width和height以外的属性是相对于视图窗口的左上角来计算的
- 如果需要获得相对于整个网页左上角定位的属性,那么只要给top、left属性加上当前的滚动位置,(通过window.scrollX和window.scrollY),这样就可以获取与当前滚动位置无关的值
IntersectionObserver交叉观察器http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/11/intersectionobserver_api.html
IntersectionObserverEntry 对象提供目标元素信息
js
{
time: 3893.92,
rootBounds: ClientRect {
bottom: 920,
height: 1024,
left: 0,
right: 1024,
top: 0,
width: 920
},
boundingClientRect: ClientRect {
// ...
},
intersectionRect: ClientRect {
// ...
},
intersectionRatio: 0.54,
target: element
}- time: 可见性发生变化的时间, 是一个高精度时间戳,单位为毫秒
- target: 被观察的元素,是一个DOM节点对象
- rootBounds: 根元素的矩形区域的信息, getBoundingClientRect()方法的返回值,如果没有根元素(即直接相对于视口滚动), 则返回null
- boundingClientRect: 当前目标元素的矩形区域信息
- intersectionRect: 目标元素与视口(或根元素)的交叉区域的信息
- intersectionRatio: 目标元素的可见比例, 即intersectionRect占boundingClientRect的比例,完全时可为1, 完全不可见时小于等于0

上图中,灰色的水平方框代表视口, 深红色的区域代表四个被观察的元素,